Crosstab Reports
Use crosstab reports, also known as matrix reports, to show the relationships between three or more query items. Crosstab reports show data in rows and columns with information summarized at the intersection points.
General use case
Here is a general use case:
from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
from django.db.models import Sum
from slick_reporting.views import ReportView
class CrosstabReport(ReportView):
report_title = _("Cross tab Report")
report_model = SalesTransaction
group_by = "client"
date_field = "date"
columns = [
"name",
"__crosstab__",
# You can customize where the crosstab columns are displayed in relation to the other columns
ComputationField.create(Sum, "value", verbose_name=_("Total Value")),
# This is the same as the calculation in the crosstab,
# but this one will be on the whole set. IE total value.
]
crosstab_field = "product"
crosstab_columns = [
ComputationField.create(Sum, "value", verbose_name=_("Value")),
]
Crosstab on a Traversing Field
You can also crosstab on a traversing field. In the example below we extend the previous crosstab report to be on the product sizes
class CrosstabWithTraversingField(CrosstabReport):
crosstab_field = "product__size"
Customizing the crosstab ids
You can set the default ids that you want to crosstab on, so the initial report, ie without user setting anything, comes out with the values you want
class CrosstabWithIds(CrosstabReport):
def get_crosstab_ids(self):
return [Product.objects.first().pk, Product.objects.last().pk]
Customizing the Crosstab Filter
For more fine tuned report, You can customize the crosstab report by supplying a list of tuples to the crosstab_ids_custom_filters attribute.
The tuple should have 2 items, the first is a list of Q object(s) -if any- , and the second is a dict of kwargs filters . Both will be passed to the filter method of the report_model.
Example:
class CrosstabWithIdsCustomFilter(CrosstabReport):
crosstab_ids_custom_filters = [
(~Q(product__size__in=["extra_big", "big"]), dict()),
(None, dict(product__size__in=["extra_big", "big"])),
]
# Note:
# if crosstab_ids_custom_filters is set, these settings has NO EFFECT
# crosstab_field = "client"
# crosstab_ids = [1, 2]
# crosstab_compute_remainder = True
Customizing the verbose name of the crosstab columns
Similar to what we did in customizing the verbose name of the computation field for the time series,
Here, We also can customize the verbose name of the crosstab columns by Subclass ComputationField and setting the crosstab_field_verbose_name attribute on your custom class.
Default is that the verbose name will display the id of the crosstab field, and the remainder column will be called “The remainder”.
Let’s see two examples on how we can customize the verbose name.
Example 1: On a “regular” crosstab report
class CustomCrossTabTotalField(ComputationField):
calculation_field = "value"
calculation_method = Sum
verbose_name = _("Sales for")
name = "sum__value"
@classmethod
def get_crosstab_field_verbose_name(cls, model, id):
if id == "----": # 4 dashes: the remainder column
return _("Rest of Products")
name = Product.objects.get(pk=id).name
return f"{cls.verbose_name} {name}"
class CrossTabReportWithCustomVerboseName(CrosstabReport):
crosstab_columns = [CustomCrossTabTotalField]
Example 2: On the crosstab_ids_custom_filters one
class CustomCrossTabTotalField2(CustomCrossTabTotalField):
@classmethod
def get_crosstab_field_verbose_name(cls, model, id):
if id == 0:
return f"{cls.verbose_name} Big and Extra Big"
return f"{cls.verbose_name} all other sizes"
class CrossTabReportWithCustomVerboseNameCustomFilter(CrosstabWithIdsCustomFilter):
crosstab_columns = [CustomCrossTabTotalField2]
Example
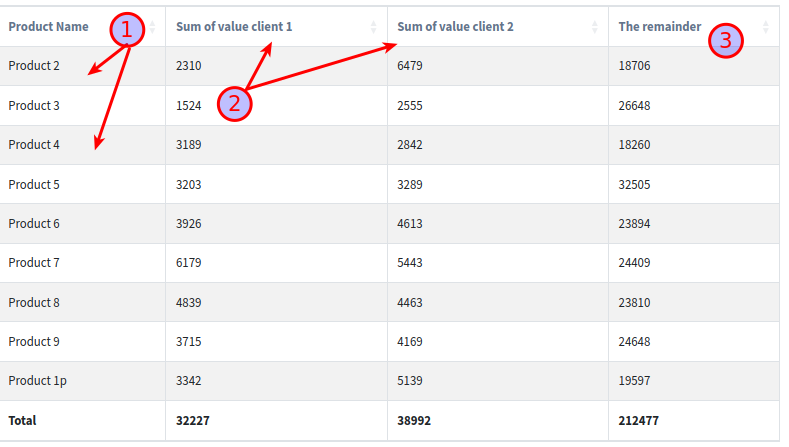
The Group By. In this example, it is the product field.
The Crosstab. In this example, it is the client field. crosstab_ids were set to client 1 and client 2
The remainder. In this example, it is the rest of the clients. crosstab_compute_remainder was set to True